Artificial intelligence is no longer science fiction. AI in Business now drives growth across the United States. From Silicon Valley startups to Wall Street banks, companies rely on smart systems to analyze data, automate work, and predict outcomes. The rise of AI tools for business has reshaped strategy, speed, and scale.
Today, leaders focus on How AI improves business efficiency and long-term value. According to research from mckinsey, companies using AI at scale report higher productivity and faster innovation cycles. These numbers reflect strong AI investment growth statistics and clear momentum toward intelligent automation.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Business?
Artificial Intelligence in business means using smart software that learns from data and improves over time. Instead of fixed rules, these systems evolve. They power Business automation, support AI-driven decision making, and strengthen Data-driven business models across industries.
In simple terms, AI in Business uses data to think faster than humans. It studies patterns, predicts risks, and recommends actions. The Role of artificial intelligence in modern enterprises includes forecasting revenue, detecting fraud, and enabling AI-powered business processes that adapt in real time.
Traditional software follows strict instructions. AI systems learn from experience. For example, accounting software records numbers. An AI system predicts cash flow gaps. This difference fuels smarter strategy and measurable AI ROI (Return on Investment).
Brief Overview of Artificial Intelligence
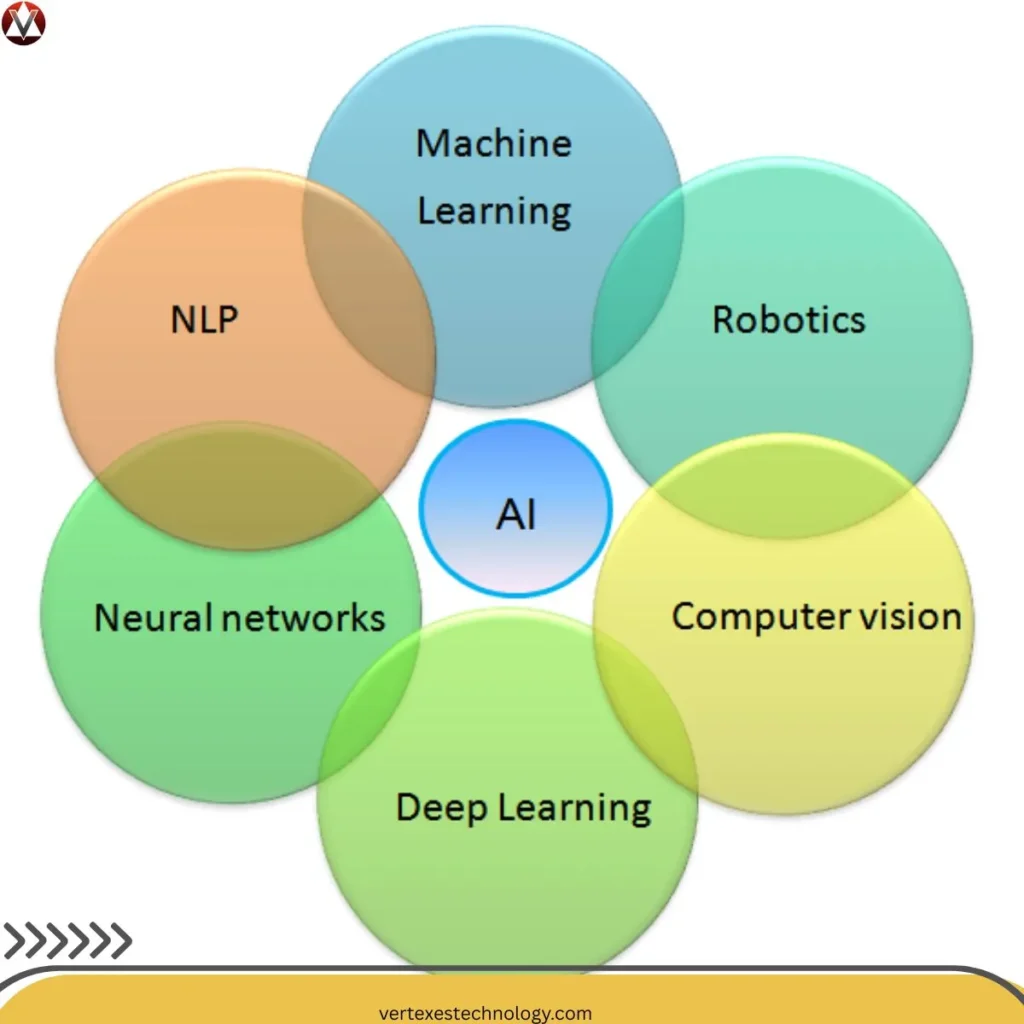
At its core, AI includes Machine Learning, deep neural networks, and language models. Machine learning in business analyzes trends for forecasting and segmentation. Deep learning applications process images, voice, and complex patterns that humans may miss.
Natural language processing in business allows software to understand text and speech. This drives AI-powered chatbots and smarter communication tools. Computer vision technology identifies defects in factories and tracks inventory visually. Meanwhile, Generative AI in business creates reports, marketing copy, and even software code.
Below is a simplified comparison of major AI branches used in enterprises:
| AI Technology | Business Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Machine Learning | Forecasting | Sales prediction |
| Deep Learning | Image analysis | Fraud detection |
| NLP | Communication | Virtual assistants |
| Computer Vision | Quality control | Factory inspection |
| Generative AI | Content creation | Automated reports |
Scaling from pilot to production requires planning. Companies build a clear AI transformation roadmap. They invest in Hybrid cloud AI infrastructure to manage vast data volumes. Proper AI model training and deployment ensures accuracy and trust.
Key Benefits of AI in Business
First and foremost, the biggest benefits of AI in business appear in productivity and precision. For example, firms deploy automating repetitive tasks with AI to reduce errors. As a result, this shift increases AI for operational efficiency and strengthens enterprise automation systems.
Moreover, cost savings follow naturally. For instance, predictive maintenance reduces downtime, while smart supply systems optimize inventory. In addition, leaders gain faster insights through AI in decision support systems. Consequently, this strengthens strategy and fuels AI-driven innovation.
Customer experience also improves. Recommendation engines enhance personalization. Support tools enable AI-based customer experience optimization and continuous engagement. When companies combine automation with insight, they unlock sustainable AI scalability in enterprises.
Real-World AI in Business Examples
Real impact appears across industries. In retail, AI in marketing and sales predicts demand and personalizes ads. Banks rely on AI in cybersecurity and advanced AI security and fraud detection to stop threats instantly.
Customer support transformed dramatically. Businesses use AI for customer service through conversational bots. These systems operate nonstop. They reduce wait times and boost satisfaction. Meanwhile, AIOps (AI for IT operations) monitors networks in real time.
Supply chains also benefit. AI in supply chain management uses Predictive analytics to anticipate shortages. Content teams adopt AI content generation to accelerate campaigns. These are powerful Real-world Artificial Intelligence business examples that prove tangible value.
AI in Business Use Cases by Industry
Healthcare providers use AI for diagnostics and patient insights. Similarly, financial firms use predictive models for trading and risk scoring. Meanwhile, retail brands build intelligent business systems that personalize every transaction.
In addition, manufacturers rely on visual inspection tools and robotics, while schools integrate adaptive learning software to enhance student outcomes. Although each sector follows unique adoption paths, AI adoption trends in companies nevertheless show steady acceleration across all industries.
Below is a simple industry impact table:
| Industry | Primary AI Benefit |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | Faster diagnostics |
| Finance | Fraud prevention |
| Retail | Personalized shopping |
| Manufacturing | Defect detection |
| Education | Adaptive learning |
Disadvantages and Challenges of AI in Business
Despite its promise, AI implementation challenges remain real. High costs limit early adoption. Skilled talent remains scarce. Poor data quality weakens models and reduces trust.
Data privacy adds complexity. Companies must build strong AI data governance frameworks. Leaders must address bias and ensure the Ethical use of AI in business. Transparent systems reduce risk and strengthen public trust.
Risk management also matters. Effective AI risk management prevents reputational harm. Smart oversight ensures compliance and fairness.
AI in Business Education and Career Opportunities
Universities now offer AI-focused business degrees. Students learn analytics, coding, and strategy. They explore Digital transformation with AI and build real-world models.
Career paths expand quickly. Roles include data scientist, AI consultant, automation architect, and analytics manager. These professionals guide AI and human workforce collaboration to maximize value.
AI in Business Research and Publications
Top research institutions publish insights on enterprise AI. Harvard Business Review frequently examines AI-driven decision making. Consulting firms publish annual reports on automation impact.
Thought leaders emphasize strategy over hype. They highlight measurable results and disciplined execution. Their findings reinforce that smart adoption fuels sustainable advantage.
Future of AI in Business
The future of AI in Business looks dynamic. Autonomous agents will manage workflows. Real-time analytics will dominate boardroom discussions. Emerging systems will integrate deeper into daily operations.
Long-term success depends on alignment. Companies must combine technology with culture. Strong leadership and continuous learning drive durable transformation. When firms invest wisely, they secure lasting growth.
Conclusion: Is AI the Future of Business?
The answer is simple. Yes. AI in Business reshapes competition and innovation. It strengthens productivity and strategy. Companies that act early gain lasting advantage. Those who hesitate risk falling behind.
Final Thoughts
Artificial intelligence stands at the heart of modern enterprise. Smart planning converts technology into measurable impact. Clear governance ensures safety and trust. When organizations combine insight with action, AI becomes a powerful growth engine.