Shingled Technology Explained has become a defining topic in modern solar energy because homeowners and businesses in the United States want more power from limited roof space. This approach belongs to next-generation solar panel technology and focuses on smarter design rather than simply larger panels. Think of it like roof shingles on a house, layered carefully to block rain more effectively.
At its core, Shingled Technology Explained shows how solar manufacturers improved efficiency, durability, and appearance at the same time. By rethinking how cells connect, engineers unlocked higher energy yield per square meter, better reliability, and stronger long-term value. That combination explains why interest in shingled designs keeps rising across residential and commercial markets.
What Is Shingled Technology in Solar Panels?

Shingled Technology Explained in solar panels refers to shingled solar panel technology where cells are cut into strips and laid in an overlapping pattern. This photovoltaic cell overlap increases the solar panel active surface area that captures sunlight. Unlike older designs, this method removes wasted gaps between cells.
These panels belong to shingled photovoltaic modules and shingled PV panels categories. They rely on conductive adhesive solar cells rather than metal ribbons. The result is busbar-free solar panels that look cleaner and perform better. For U.S. rooftops, this means more power without expanding roof size.
How Shingled Solar Cell Interconnection Works
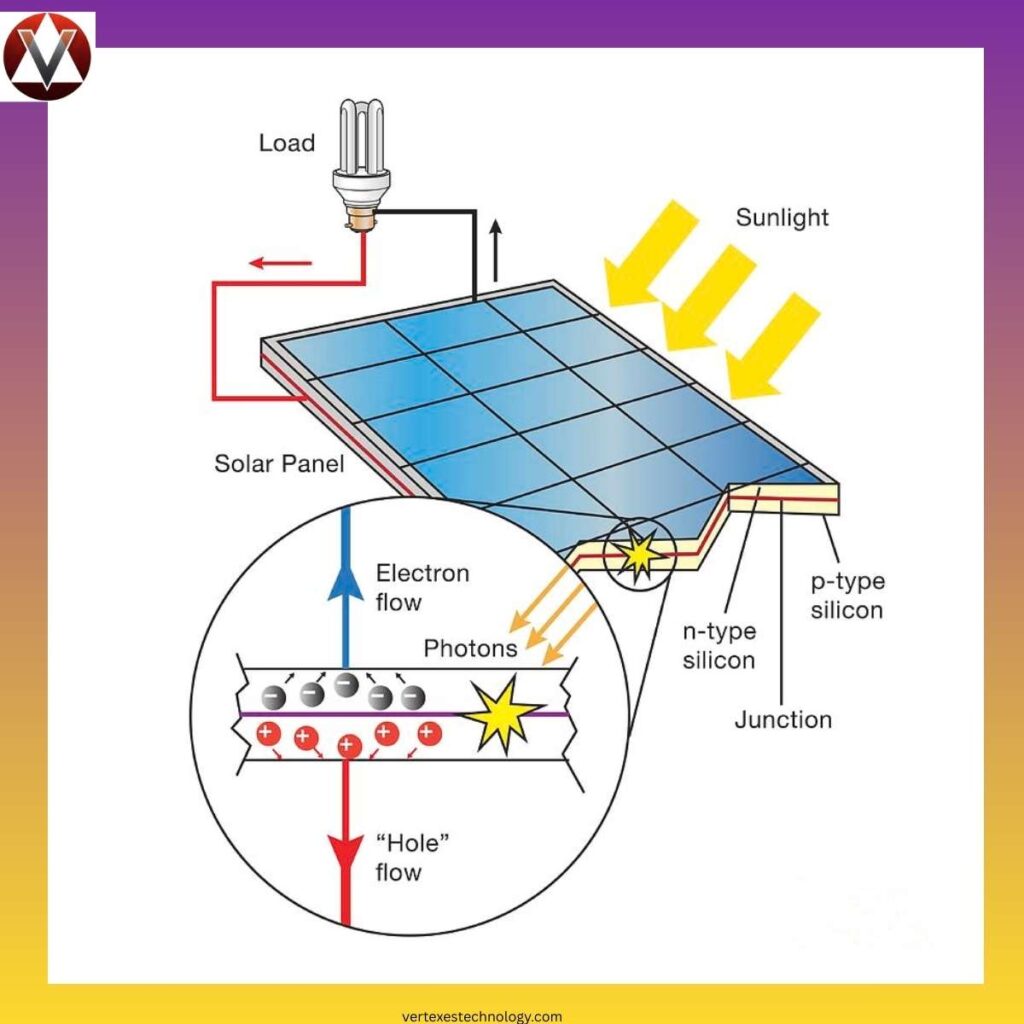
The heart of Shingled Technology Explained is shingled solar cell interconnection. Manufacturers use laser-cut solar cells through ultra-precise laser scribing. This solar cell strip cutting divides one large cell into smaller strips that reduce resistance.
Each strip connects using direct solar cell interconnection and cell-to-cell electrical connection. These strips form parallel-connected solar cell columns using a series and parallel cell configuration. Power flows through shorter paths, delivering improved current flow and reduced electrical resistance across the panel.
Difference Between Shingled Technology and Traditional Solar Panels

Traditional panels use ribbons and busbars that block light and add resistance. Shingled vs conventional solar panels comparisons show how older designs lose efficiency over time. Heat and stress often damage solder joints, reducing output.
In contrast, shingled PV panels eliminate these weaknesses through elimination of busbars and weld-free solar cell connection. This advanced photovoltaic interconnection boosts solar module output power improvement while supporting performance degradation reduction across decades.
Role of Electrically Conductive Adhesives (ECA) in Shingled Panels
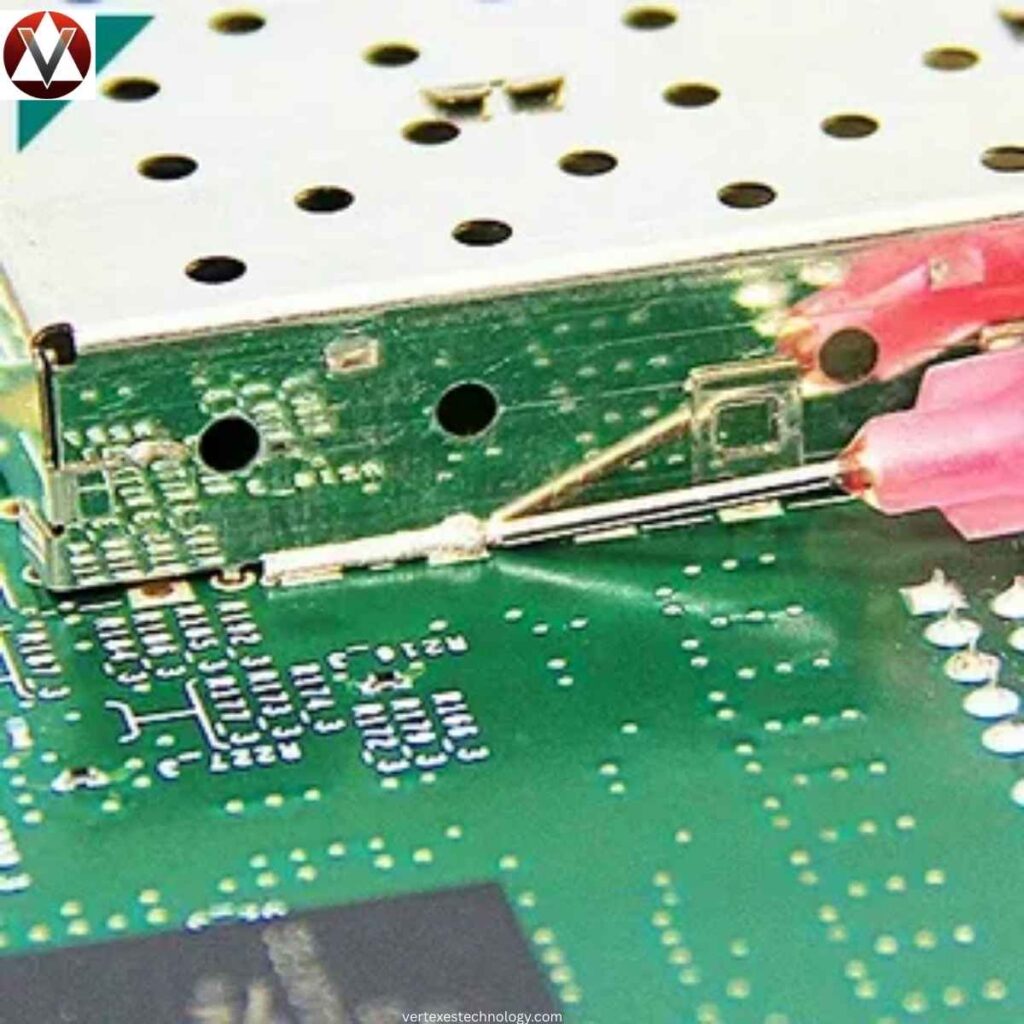
A key part of Shingled Technology Explained is Electrically Conductive Adhesive (ECA). This conductive glue instead of soldering bonds strips together while carrying electricity. It supports solder-free interconnection and front-side metal ribbon elimination.
Because ECAs cure at lower temperatures, they allow low-temperature processing. This improves mechanical stress reduction, supports flexibility of solar cells, and strengthens enhanced module reliability. Panels last longer and resist environmental damage more effectively.
Key Benefits of Shingled Solar Panel Technology
More Power Output per Surface Area
By using overlapping solar cells, shingled designs increase the increased active photovoltaic area. This directly delivers higher power output per square meter. U.S. homeowners gain more energy without adding panels.
Optimized Space Utilization
These panels are space-efficient solar panels built for optimized rooftop solar installations. Urban homes benefit most because every inch of roof counts. Fewer panels meet the same energy goals.
Lower Electrical & Ohmic Losses
Shorter current paths create reduced resistive loss solar cells. This leads to ohmic loss reduction in PV modules. Energy flows smoothly with minimal waste.
Better Performance in High Temperatures
Shingled designs improve improved thermal behavior and lower operating temperature. These temperature-resilient solar modules maintain high-temperature performance stability in hot U.S. climates.
Improved Shade Tolerance
The layout enhances partial shading solar panel performance. Power reroutes around shaded areas, delivering better shade tolerance and consistent output.
Reduced Micro-Cracks & Longer Lifespan
These are micro-crack resistant solar panels designed for solar panel mechanical stress resistance. They show strong expansion and contraction resistance and long-term module reliability.
Clean Aesthetic & Modern Design
The absence of ribbons creates aesthetic solar panel design. A uniform panel surface appeals to homeowners seeking premium photovoltaic panels with visual harmony.
Performance and Efficiency Gains in Shingled Solar Modules
Shingled Technology Explained consistently shows measurable efficiency gains. Many high-efficiency solar panels exceed traditional output using active photovoltaic area optimization. This translates to increased energy yield year after year.
| Feature | Traditional Panels | Shingled Panels |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency Stability | Moderate | High |
| Heat Resistance | Limited | Strong |
| Shade Impact | High Loss | Low Loss |
These gains support improved ROI in solar installations and long-term electricity cost savings.
Reliability, Durability, and Mechanical Advantages
Shingled modules resist wind, snow, and heat thanks to mechanical stress tolerance and wind load flexibility. The reduced ribbon failure risk improves improved electrical stability.
This design supports solar module durability and enhanced module lifespan. Many systems carry a long-term performance guarantee, reassuring U.S. buyers focused on value.
Manufacturing Process and Technological Challenges
The shingling manufacturing workflow requires precision. Solar module assembly process steps must align strips accurately using minimal overlap cell design. Small errors affect output.
Manufacturers also manage adhesive curing and quality control. Despite challenges, this next-generation solar module design continues gaining adoption across commercial solar panel technology sectors.
Shingled Solar Panels for Commercial and Residential Applications
For homes, residential high-efficiency solar panels maximize limited space. For businesses, high power density solar modules support commercial solar investment strategies.
Both markets benefit from solar ROI optimization and reduced payback period. Over time, users see business solar efficiency gains with stable output.
Real-World Example: Recom Puma Shingled Solar Panel
The Recom Puma solar panel demonstrates Shingled Technology Explained in action. It combines high-reliability solar panels, strong efficiency, and solid warranties.
Recom’s design highlights how high-efficiency solar module brands deliver performance with visual appeal. It reflects why shingled designs dominate premium markets.
Shingled Technology vs Other “Shingled” Terms (SMR, HDD, Shingles)
Many confuse solar shingling with data storage like SMR hard drives or medical shingles. Shingled vs HJT solar technology, shingled vs monocrystalline panels, and shingled vs PERC technology comparisons belong only to solar energy.
Shingled Technology Explained here focuses strictly on photovoltaics. Understanding this difference helps buyers make informed decisions without confusion.
FAQs
Are shingled solar panels better?
Yes, shingled solar panels are better in efficiency and reliability because they reduce electrical losses and perform well in heat and partial shade.
Which is better, TOPCon or Bifacial?
Neither is universally better; TOPCon improves cell efficiency while bifacial panels generate extra power from reflected light, making site conditions the deciding factor.
Is a 90% efficient solar panel possible?
No, current solar technology cannot reach 90% efficiency; most high-end panels today operate between 21% and 24%.
What is the solar 120% rule?
The 120% rule allows a solar system to backfeed up to 120% of a panel’s busbar rating when properly sized and protected.
Is 10 kW enough to run a house?
Yes, a 10 kW solar system can power an average U.S. home, depending on energy usage, sunlight, and location.
What is the 125% rule in electricity?
The 125% rule requires electrical conductors and breakers to be sized at 125% of continuous loads for safety.
What are the disadvantages of shingles?
Solar shingles usually cost more, are harder to repair, and may offer lower efficiency compared to traditional solar panels.
What are the top 3 solar panels?
Popular high-performance options include SunPower Maxeon, REC Alpha, and LG NeON, based on efficiency and reliability.
How long do solar shingles last?
Most solar shingles last 25 to 30 years, with gradual power output decline over time.
Final Thoughts
Solar technology keeps moving forward, and shingled solar panels are a strong example of smart engineering done right. They deliver higher efficiency, better heat and shade performance, and improved durability without needing more roof space. For homeowners and businesses focused on long-term value, reliability, and clean design, shingled panels are a future-ready choice.
That said, no single solar technology fits everyone. The best option depends on budget, roof layout, climate, and energy goals. Understanding how shingled technology compares with alternatives like TOPCon, bifacial, or traditional panels helps you invest with confidence and maximize returns over the system’s lifetime.


