Artificial intelligence is no longer a distant idea. It shapes daily life in the United States. From phones to hospitals, Levels of AI explain how smart these systems really are. Understanding AI intelligence levels helps people judge risks, value, and limits with clear eyes.
The evolution of artificial intelligence did not happen overnight. It moved through clear AI development stages. Each stage reflects growing artificial intelligence capabilities. This guide explains those stages in plain English, with facts, tables, and real-world clarity.
What Are the Levels of AI?

Levels of AI describe how closely machine intelligence compares to human thinking. Some systems only follow rules. Others learn patterns. A few are imagined to think like people. These divisions help experts map machine intelligence levels with precision.
This structure matters because the current state of artificial intelligence often looks smarter than it is. Grouping AI into levels explains why AI in modern technology can feel human while still lacking awareness. It also clarifies progress toward the future of artificial intelligence.
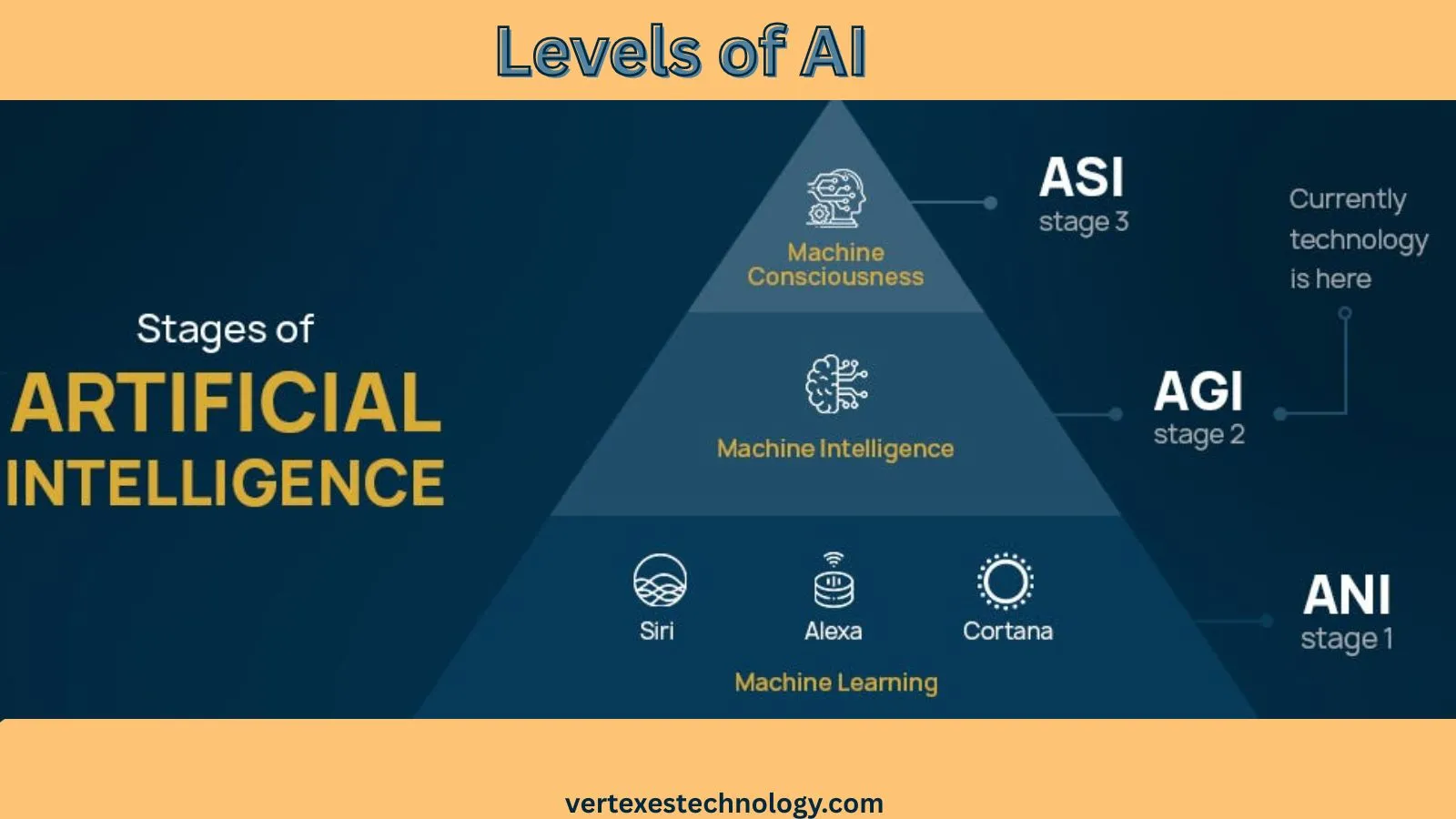
The 3 Core Levels of AI Explained
The most accepted framework splits AI into three major intelligence tiers. These tiers form the backbone of how researchers discuss AI capabilities explained today.
| AI Level | Core Ability | Status |
|---|---|---|
| ANI | Task-focused intelligence | Active today |
| AGI | Human-level reasoning | Theoretical |
| ASI | Beyond human thinking | Speculative |
This model simplifies debates about narrow AI vs general AI. It also separates real systems from science fiction dreams.
Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI) – The AI We Use Today
ANI dominates real life. In this level, artificial narrow intelligence performs specific tasks with impressive speed. These AI systems designed for single-purpose tasks excel at one job and fail outside it. This explains many weak AI examples used daily.
Examples flood daily life. Chatbots and virtual assistants powered by AI answer questions. Recommendation engines predict tastes. Self-driving cars use multiple AI models to see roads and avoid danger. These are real-world applications of narrow AI, where AI tools outperform humans in speed and efficiency.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) – Human-Level AI
AGI represents a dramatic leap. Here, general artificial intelligence human-level reasoning allows learning across fields. This aligns with the strong AI definition, where machines understand, adapt, and reason like humans.
However, current AI lacks true understanding and consciousness. No system today can transfer knowledge freely between tasks. Researchers debate is general AI possible, since human reasoning blends emotion, memory, and context in complex ways.
Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI) – Beyond Human Intelligence
ASI goes even further. Artificial super intelligence beyond human intelligence imagines systems smarter than any person. This idea fuels discussion around super intelligence AI and control risks.
Experts warn about power imbalance. Future AI systems with autonomous decision-making could reshape economics and defense. The benefits are vast, yet the dangers require caution. This stage defines long-term debates on when will artificial super intelligence exist.
What Level of AI Is ChatGPT?
ChatGPT belongs firmly to ANI. It feels flexible because of multimodal AI systems working together. Text prediction, memory patterns, and training data blend smoothly. This creates the illusion of reasoning.
Despite that, ChatGPT does not think. It reflects learned patterns. This shows limitations of current AI technology and highlights limitations of narrow AI. Intelligence here is advanced pattern matching, not awareness.
What Level of AI Are We at Now?
Humanity lives fully inside ANI. The current state of artificial intelligence shows massive productivity gains without true cognition. This stage fuels innovation across sectors.
In the U.S., AI used in healthcare, education, and manufacturing improves diagnostics, grading, and logistics. These are practical AI applications in real life, not steps toward consciousness.
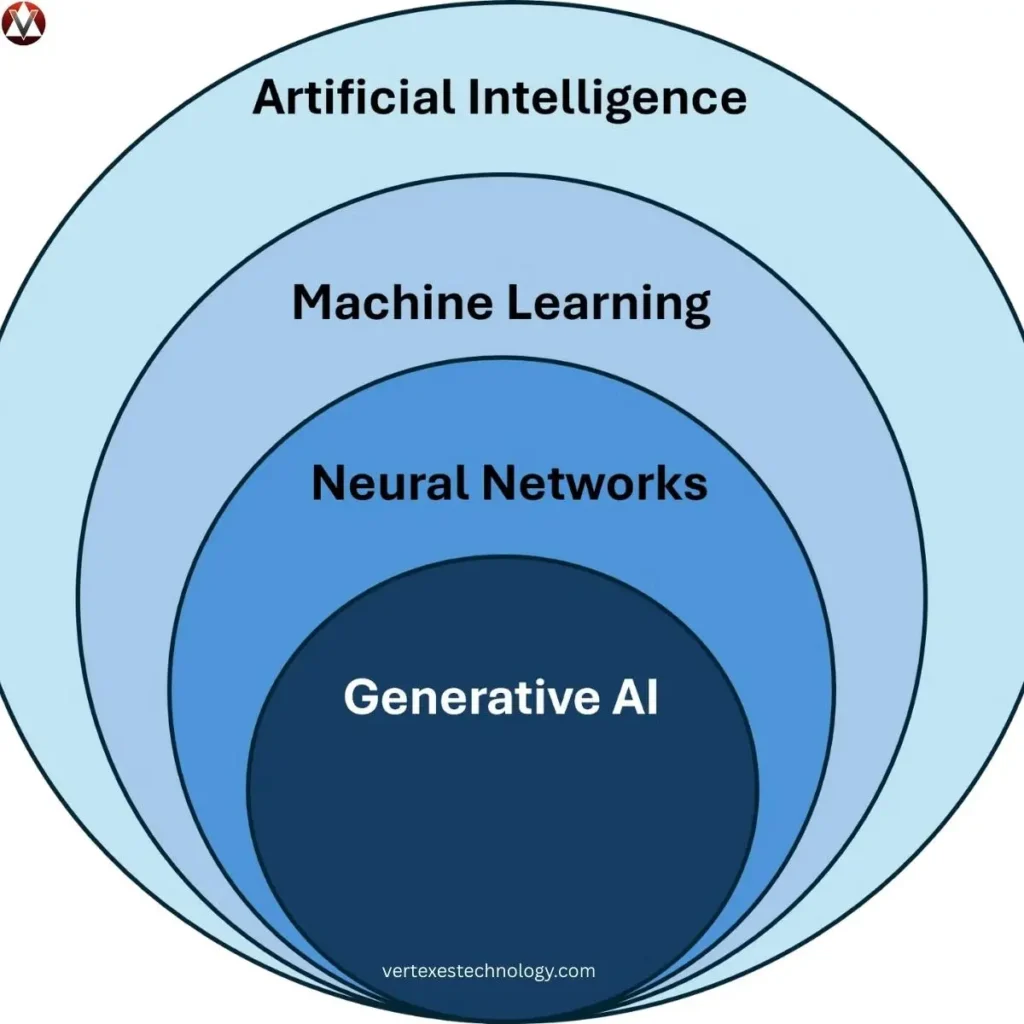
5 Main Types of Artificial Intelligence With Examples
AI types describe how systems work, not how smart they are. Understanding types of artificial intelligence avoids confusion with Levels of AI.
| AI Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Rule-Based | Fixed logic | Tax software |
| Machine Learning | Pattern learning | Fraud detection |
| Deep Learning | Neural networks | Image recognition |
| Generative AI | Content creation | ChatGPT |
| Reinforcement Learning | Trial-based learning | Game AI |
These types often combine through integration of multiple AI models in one platform.
The 7 Levels of AI – Expanded Classification
Some researchers expand AI into seven stages. These include reactive systems, memory-based systems, and hypothetical self-aware machines. This framework adds nuance to machine intelligence levels.
Only early stages exist today. Later stages remain theory. This expanded model helps explain the evolution of artificial intelligence without exaggeration.
Levels of AI Use in Education
Education benefits greatly from ANI. For example, AI personalizes learning and reduces teacher workload. In addition, it adapts content speed and difficulty with accuracy.
Furthermore, in classrooms, AI in modern technology supports tutoring tools and plagiarism detection. As a result, these systems improve outcomes without replacing educators. Overall, this practical use shows responsible progress in AI development stages..
10 Levels of AI – Concept vs Reality
Some futurists propose ten AI levels. These range from simple calculators to god-like intelligence. While imaginative, most levels lack scientific grounding.
Practical models still favor three or seven levels. Reality-driven frameworks better explain AI intelligence levels and guide policy without hype.
Types of Artificial Intelligence vs Levels of AI (Comparison Table)
| Aspect | Types of AI | Levels of AI |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | How AI works | How smart AI is |
| Scope | Technical | Conceptual |
| Usage | Development | Risk assessment |
This distinction clarifies difference between ANI AGI and ASI without confusion.
FAQs
Q1: What are the levels of AI?
The levels of AI describe how smart AI systems are, from simple task-based machines to superintelligent AI.
Q2: How many types of AI are there?
There are seven main types of AI, including rule-based AI, machine learning, deep learning, generative AI, reinforcement learning, expert systems, and robotics AI.
Q3: What level of AI is ChatGPT?
ChatGPT is Narrow AI (ANI) because it performs specific language tasks without real understanding or consciousness.
Q4: What is Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)?
AGI is human-level AI that can learn and reason across multiple tasks, but it does not exist yet.
Q5: What is Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI)?
ASI is AI that could surpass human intelligence and decision-making abilities, mostly a future concept.
Q6: What is the difference between ANI, AGI, and ASI?
ANI handles specific tasks, AGI mimics human reasoning, and ASI goes beyond human intelligence.
Q7: What is an LLM and GPT?
An LLM (Large Language Model) is AI trained on large text data, and GPT is a type of LLM that generates human-like text.
Q8: What are real-world examples of narrow AI?
Examples include chatbots, virtual assistants, self-driving cars, recommendation engines, and AI used in healthcare, education, and manufacturing.
Q9: Are we at AGI or ASI yet?
No, current AI lacks true understanding and consciousness. Today’s AI is still Narrow AI performing specific tasks efficiently.
Q10: What is the future of artificial intelligence?
The future may include AGI and ASI with autonomous decision-making, multimodal capabilities, and broader applications in all sectors.
Final Thoughts
Understanding Levels of AI removes fear and hype. In fact, today’s systems are powerful yet limited. Moreover, they enhance work, not replace humanity. Ultimately, the future of artificial intelligence depends on careful design, ethical thinking, and informed users who know what AI is and what it is not.
“The real risk is not that computers will begin to think like humans, but that humans will begin to think like computers.” — Sydney J. Harris