Is AI just like the internet? Many people ask this question because both Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the internet have transformed how we live, work, and communicate. Today,
AI in daily life powers chatbots and virtual assistants, AI-driven recommendations, and AI-powered automation across industries. Unlike the internet, which mainly connects people and information, AI uses Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), and Natural Language Processing (NLP) to make decisions, predict outcomes, and provide AI-powered insights. From business to healthcare, AI applications are shaping the future faster than the internet did, showing that while they share similarities, AI vs Internet is fundamentally different.
How AI works

AI works by analyzing large datasets using Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) models. These systems learn from examples rather than explicit programming. Natural Language Processing (NLP) allows computers to understand and generate human language, while Computer Vision enables machines to interpret visual data like images and videos. AI computational power ensures complex calculations happen in seconds, something humans cannot achieve at the same speed.
A simple analogy is teaching a child to recognize animals. Show thousands of images of dogs and cats, and the child learns patterns. Similarly, self-learning AI systems identify features in data, improving accuracy over time. Modern LLMs like GPT or Generative AI (Gen AI) models demonstrate this by producing human-like text, showing how AI human-like reasoning and AI problem-solving capabilities are applied in real-world scenarios. Is AI Just Like the Internet
AI vs. Internet: Key differences and similarities
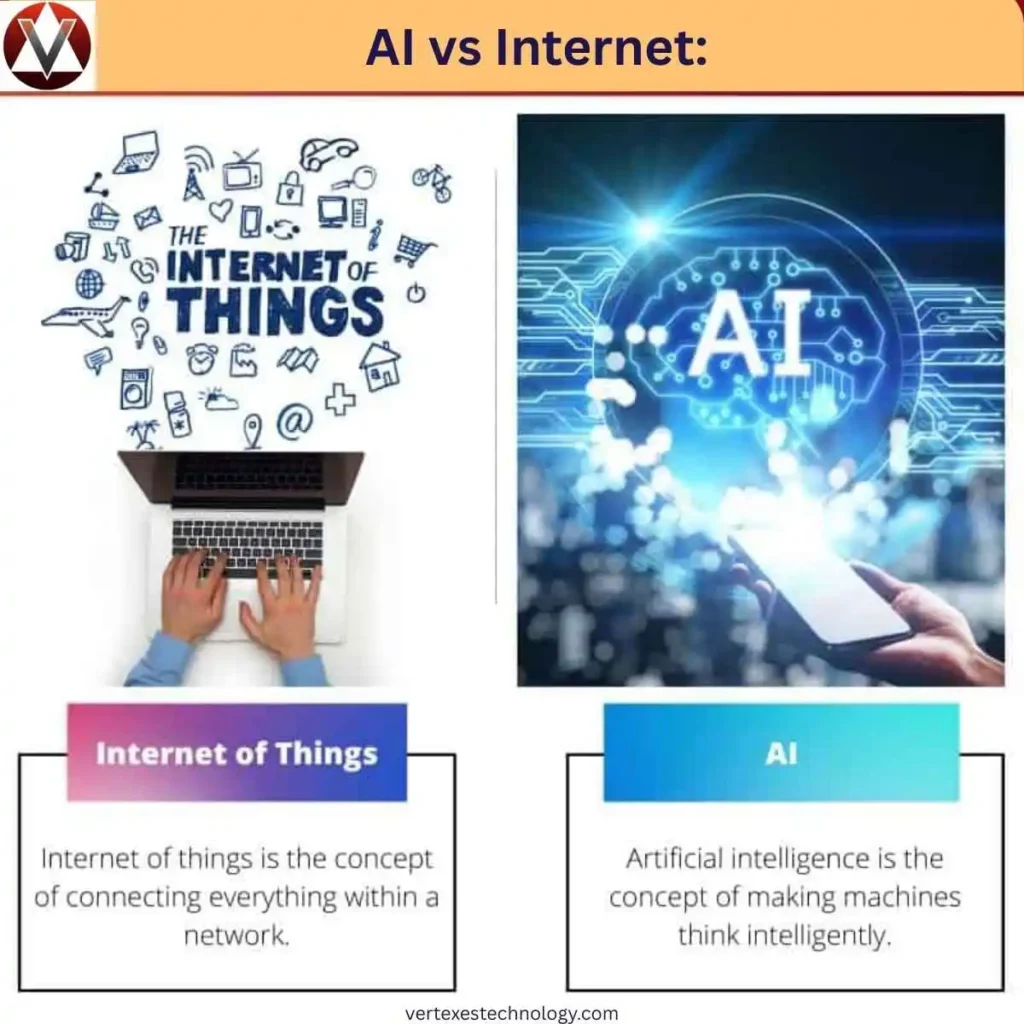
At first glance, AI vs Internet seems similar because both have transformed society. The internet connected people and information globally, while AI-powered automation adds intelligence to devices and systems. AI adoption and impact are growing rapidly, influencing industries, healthcare, and communication just as the internet revolution did decades ago. Is AI Just Like the Internet
However, AI vs human intelligence and internet capabilities differ fundamentally. The internet is a network for sharing information, while AI in business and healthcare uses data-driven decision-making to make predictions and automate tasks. Both technologies reshape daily life, but AI-enabled tools operate intelligently rather than just connect people and data.
The Evolution of AI and the Internet

A brief history of AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) started in the 1950s with neural networks and the Turing Test. Milestones include IBM’s Deep Blue defeating Garry Kasparov and the development of AI neural networks capable of pattern recognition. Recently, Generative AI (Gen AI) and Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized AI applications, showing the power of AI computational power and AI problem-solving capabilities.
Early AI capabilities and functionality were limited, but modern AI algorithms and prediction systems can handle complex tasks, from speech recognition to medical imaging. The growth of AI intelligence levels shows the rapid evolution of self-learning AI systems that now rival human decision-making in specialized areas.
How the internet changed the world
The internet transformed communication, commerce, and access to knowledge. Social media, streaming, and e-commerce changed lifestyles globally. Its wide accessibility allowed information to travel instantly, creating an AI adoption and impact template that AI-powered insights now follow.
The internet also enabled the rise of data-driven decision-making. Companies use analytics to improve services, much like AI-driven recommendations do today. Both technologies encourage innovation, but while the internet connects, AI in daily life interprets and predicts based on that connection.
Parallels in adoption and societal impact
Both AI and the internet share rapid adoption and transformative effects. Businesses implement AI-powered automation similarly to how they embraced online platforms. For example, banks now rely on AI algorithms and prediction for fraud detection, just as they use the internet for online banking.
Society experiences shifts in skills, ethics, and regulations with both. Ethical AI and bias challenges mirror early internet privacy concerns. These parallels show how AI intelligence levels evolve in a connected, global ecosystem.
Types of AI
AI by capability: Narrow, General, Super intelligent
ANI (Artificial Narrow Intelligence) focuses on one task, like facial recognition technology or AI-powered automation in chatbots. AGI (Artificial General Intelligence) aims to mimic AI human-like reasoning across multiple tasks. ASI (Artificial Superintelligence) is theoretical but represents a future where self-learning AI systems surpass human intelligence. Is AI Just Like the Internet
Currently, ANI dominates AI applications, while AGI and ASI remain research topics. Understanding AI capabilities and functionality helps set realistic expectations about AI’s role compared to the internet.
AI by functionality: Reactive, Limited Memory, Self-learning
Reactive machines perform predefined tasks with no memory, like early chess programs. Limited memory AI adapts based on short-term data, common in self-driving cars. Self-learning AI systems, like Generative AI (Gen AI) models, continuously improve through pattern recognition and predictive analytics, enabling intelligent decision-making in business and healthcare.
Common Misconceptions About AI
Myth: AI is conscious and has feelings
Despite what movies show, AI vs human intelligence is not emotional. Smart machines follow AI algorithms and prediction without subjective experience. People often confuse self-learning AI systems with sentience, but AI lacks true consciousness. Is AI Just Like the Internet
Myth: AI is always objective and unbiased
Ethical AI and bias are crucial issues. Poor AI training data can lead to unfair outcomes in hiring, credit, or healthcare. Recognizing this helps organizations implement AI ethics and regulation. Is AI Just Like the Internet
Myth: AI will replace all human jobs
While AI-powered automation handles repetitive tasks, humans remain vital for creativity, leadership, and judgment. Studies show AI often complements work rather than replaces it, creating new roles requiring oversight of AI-enabled tools.
AI Applications in Real Life
Business and industry automation
Businesses use AI in business and healthcare to optimize supply chains, finance, and customer service. Data-driven decision-making allows faster, smarter operations, and AI-driven recommendations improve productivity across sectors.
Healthcare and research breakthroughs
AI in daily life extends to medicine, where Computer Vision assists in imaging and diagnostics. Predictive analytics predicts disease outbreaks, while Natural Language Processing (NLP) helps analyze patient records, making healthcare faster and safer.
AI in everyday consumer tech
From chatbots and virtual assistants to speech and language recognition on smartphones, AI improves convenience. Smart machines suggest products, automate home devices, and personalize experiences, making AI as influential as the internet in daily routines.
AI and the Internet: Comparing Impact
Speed of adoption and global influence
The internet spread quickly across the globe, connecting millions. Similarly, AI adoption is accelerating through AI applications and AI-enabled tools. Companies leverage AI to analyze data and predict trends faster than ever.
Access, availability, and connectivity
Unlike the internet, AI requires computational power and quality AI training data. Yet, cloud platforms and open-source LLMs increase accessibility. Both technologies empower AI-powered insights but operate differently in reach and infrastructure.
Risks, regulation, and ethical considerations
AI introduces AI ethics and regulation challenges, from bias to privacy. Unlike the mostly open internet, AI decisions can have irreversible consequences, making governance vital. Proper rules ensure self-learning AI systems serve society ethically.
Benefits and Challenges of AI
Efficiency, speed, and reducing human error
AI enhances accuracy in industries. AI algorithms and prediction reduce mistakes, while AI-powered automation increases efficiency in finance, healthcare, and logistics.
Automation of repetitive tasks
Routine tasks like data entry, scheduling, or monitoring systems are handled by AI-enabled tools, freeing humans to focus on creativity and strategy.
Ethical, privacy, and bias concerns
Bias in AI training data can lead to unfair results. Companies must follow AI ethics and regulation to maintain trust and ensure AI-driven recommendations remain unbiased.
The Future of AI
Generative AI, LLMs, and AI agents
Generative AI (Gen AI) and Large Language Models (LLMs) are reshaping content creation, research, and business workflows. These systems demonstrate advanced AI problem-solving capabilities and AI human-like reasoning.
How AI might evolve differently from the internet
Unlike the internet, AI can learn, adapt, and predict autonomously. Its growth depends on AI computational power, AI training data, and human oversight, making it potentially more transformative.
Opportunities for businesses and society
AI offers efficiency, predictive insights, and improved healthcare outcomes. Companies leveraging AI in business and healthcare gain strategic advantages while society benefits from better services and automation.
Resources, Tools, and Getting Started
Recommended AI platforms and services
Google Cloud AI, Microsoft AI, and OpenAI tools provide accessible AI-enabled tools. Companies can implement AI-powered automation without heavy infrastructure.
Learning resources for AI beginners
Free courses, tutorials, and communities help beginners explore Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), Natural Language Processing (NLP), and Computer Vision. Hands-on practice is key.
How to integrate AI safely into your workflow
Start small, monitor outcomes, and ensure ethical use. Using AI algorithms and prediction responsibly ensures AI-powered insights deliver value without risks.
FAQs
Is AI like the internet?
No, AI is a technology that learns and predicts, while the internet is a network for sharing information; they complement but are not the same.
Is AI possible without the internet?
Yes, AI can run locally on computers or servers, but the internet enables cloud AI, data sharing, and faster updates.
Which 3 jobs will survive AI?
Creative roles, emotional intelligence jobs (like therapists), and complex strategic decision-making roles are least likely to be replaced.
Is AI 100% truthful?
No, AI relies on data and algorithms, so it can be biased, inaccurate, or misinformed depending on the input.
Which country is #1 in AI?
The United States leads in AI research, development, and investment, closely followed by China.
What is the 30% rule in AI?
It refers to a guideline suggesting AI models should handle around 30% of tasks automatically while humans oversee the rest for accuracy.
What is AI’s biggest weakness?
AI depends heavily on quality training data, lacks true understanding, and can be biased or manipulated.
What did Stephen Hawking say about AI?
He warned that AI could be the “worst event in human history” if not managed carefully, emphasizing risks of uncontrolled superintelligence.
Which country is no 1 in internet speed?
As of recent reports, Singapore consistently ranks #1 in average internet speed worldwide.
Conclusion
AI and the internet both transformed society, but AI vs Internet differs fundamentally. While the internet connects people and information, AI interprets, predicts, and acts using self-learning AI systems and AI-enabled tools. Both are vital for the future.
AI intelligence levels continue to evolve, promising more impact than the internet in certain areas. Generative AI (Gen AI), LLMs, and AI in daily life show that AI is not just a network like the internet but a transformative, intelligent system shaping the future.