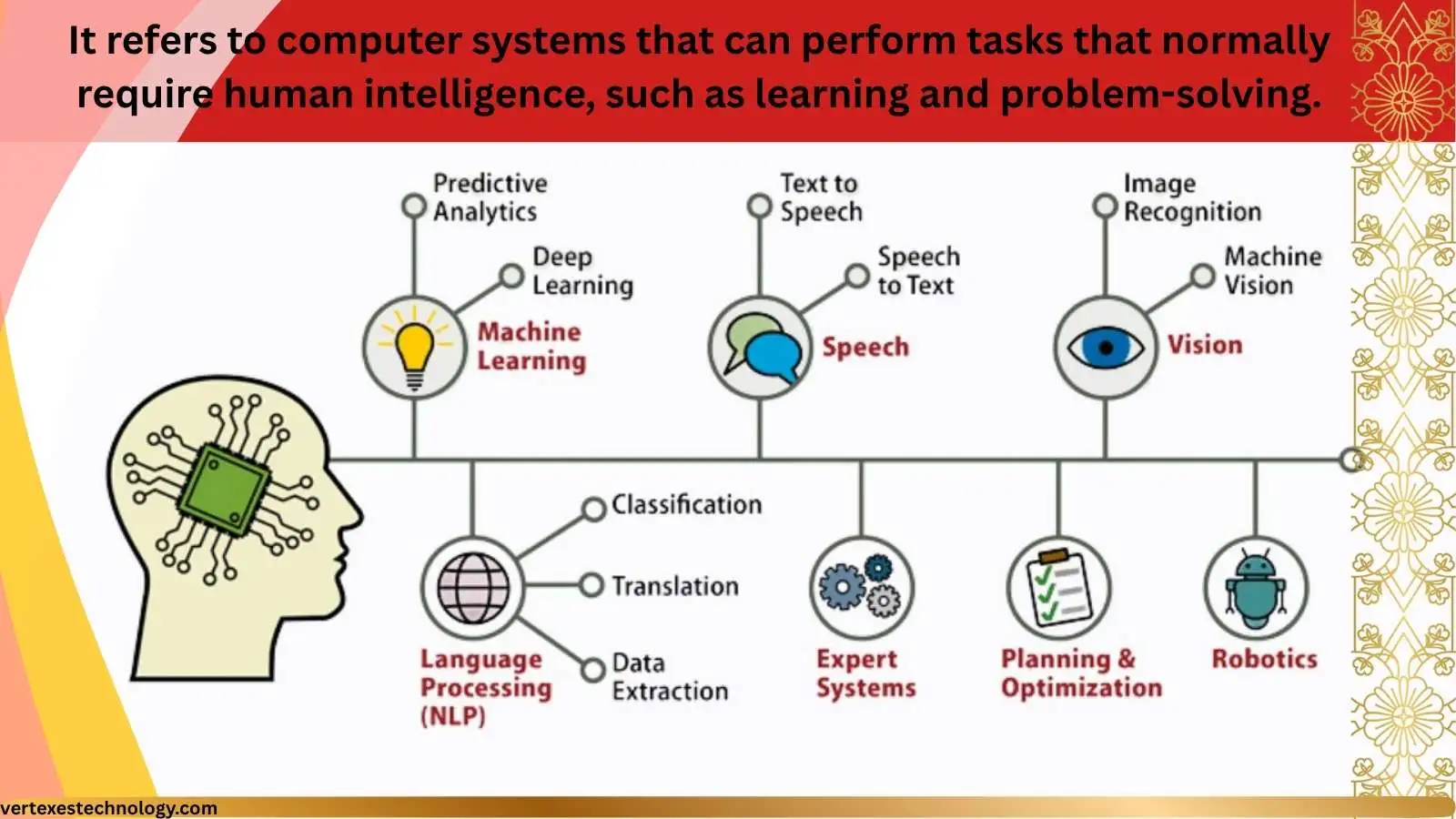
Artificial intelligence has moved from research labs into everyday American life. From phones to hospitals, machines now assist human decisions at scale. To truly understand this shift, you must understand the Levels of AI, also known as artificial intelligence levels or AI capability levels. These levels explain how intelligent systems grow from basic automation into advanced cognitive entities.
This article explains what are the levels of AI, how AI intelligence levels are defined, and why the evolution of artificial intelligence matters for the future of work, education, transportation, and innovation in the United States.
Understanding Artificial Intelligence (AI) – A Strong Foundation

Artificial intelligence describes computer systems that mimic aspects of human intelligence comparison, including learning, reasoning, and perception. Experts organize AI into stages of artificial intelligence to explain how machines evolve from simple instruction-following tools into adaptive systems. These Levels of AI help researchers and policymakers understand risks, benefits, and limitations.
The early AI development stages relied heavily on rule based AI, where machines followed predefined logic. Over time, advances in machine learning models and deep learning applications enabled systems to learn from data. Today, most deployed systems still fall under weak AI or weak artificial intelligence, meaning they perform specific tasks rather than general reasoning.
The 7 Levels of Artificial Intelligence Explained (Core Section)
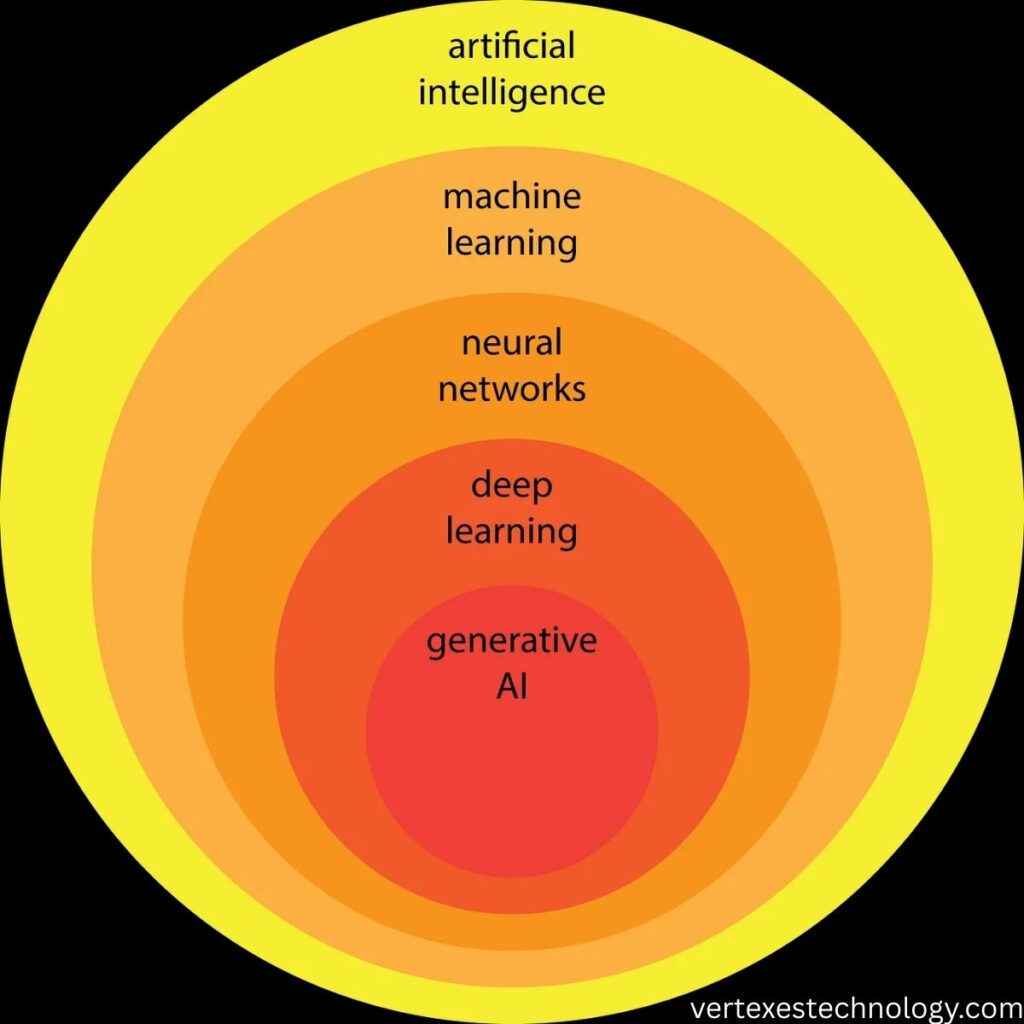
The Levels of AI framework divides intelligence into progressive capability tiers. These artificial intelligence levels explain how systems grow in autonomy, learning depth, and reasoning power. Each level represents a step forward in AI decision making and adaptability.
Early levels focus on task automation and structured logic. Higher levels introduce data driven intelligence, feedback loops, and self learning AI systems. The final levels explore theoretical concepts such as machine consciousness and artificial consciousness, which remain under active research and debate.
Level 5 – Deterministic AI & Static Optimization
Level 5 systems focus on predictable environments where outcomes can be mathematically optimized. This stage uses deterministic logic to select the best action from known options. These AI intelligence levels excel in logistics, supply chains, and engineering design.
In practice, Level 5 systems power routing software, energy optimization, and industrial scheduling. For example, trucking companies use static optimization to reduce fuel costs. These systems demonstrate strong problem solving AI, yet they cannot adapt beyond predefined constraints.
Level 6 – Sequential Decision-Making AI
Level 6 AI introduces learning through experience. These systems analyze previous outcomes to guide future actions. Reinforcement learning allows machines to improve through trial and feedback, enabling autonomous decision making in dynamic environments.
This level supports self driving cars, robotics, and game-playing systems. For instance, autonomous vehicles learn to navigate traffic using machine perception and reward-based models. These systems act as intelligent agents, constantly refining decisions in real time.
Level 7 – Reasoning, Creativity & Judgment (Advanced AI / AGI)
Level 7 represents Artificial General Intelligence or AGI, where machines demonstrate flexible reasoning comparable to humans. This level includes abstract thinking, creativity, and moral judgment. Experts often ask is AGI possible, as no system has reached this stage yet.
AGI would enable cognitive reasoning systems capable of learning any intellectual task. This level raises ethical questions about control, safety, and alignment. Researchers also debate what comes after AGI, often referencing Artificial Super Intelligence and AI beyond human intelligence.
Main Types of Artificial Intelligence (With Real Examples)

While Levels of AI describe capability growth, types of artificial intelligence describe scope. Understanding how AI intelligence is classified requires examining ANI, AGI, and ASI. These categories explain whether a system performs one task or many.
Most current systems fall under Artificial Narrow Intelligence, while Artificial General Intelligence and Artificial Super Intelligence remain theoretical. This distinction helps explain are we in the age of narrow AI and why most systems remain task-bound.
Narrow AI (ANI) – Examples
Narrow AI, also called ANI, refers to narrow artificial intelligence built for specific tasks. These systems are examples of task specific AI and single purpose AI systems. They dominate today’s market.
Examples include AI powered chatbots, virtual assistants, Alexa and Siri, recommendation engines, and manufacturing robots. These systems demonstrate strong performance in one domain but lack general understanding.
General AI (AGI) – Examples
General AI or AGI refers to systems with human level intelligence across domains. Such systems could reason, learn, and adapt without task-specific programming. No real-world AGI exists today.
Researchers experiment with multimodal AI systems and multimodal AI models to approach this goal. These efforts attempt to combine vision, language, and reasoning into unified intelligence.
Super AI (ASI) – Future Concept
Super AI or ASI describes intelligence that surpasses humans in all cognitive areas. This includes superintelligent machines capable of innovation beyond human limits. ASI is purely hypothetical today.
Experts debate the risks of AI beyond human intelligence, including control loss and societal disruption. This concept fuels global discussions about governance and AI safety.
Real-World Applications of AI by Industry
The Levels of AI appear differently across industries. Lower levels dominate consumer tools, while higher levels support automation in critical systems. Understanding these applications helps organizations choose safe, effective solutions.
Industries adopt AI based on risk tolerance, regulation, and data availability. The table below summarizes common applications.
| Industry | Typical AI Level | Example Use |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Level 4–6 | Diagnostics and AI in healthcare |
| Education | Level 3–5 | Personalized learning |
| Transportation | Level 5–6 | Autonomous routing |
| Government | Level 3–5 | Public service automation |
Levels of AI Use in Education
AI in education focuses on personalization and efficiency. Systems analyze student data to adapt content and pace. These tools rely on data driven intelligence rather than general reasoning.
Adaptive tutoring platforms and grading tools help teachers save time. However, these systems remain weak AI, lacking deep understanding or creativity.
AI in Trucking & Transportation
Transportation relies heavily on optimization and prediction. AI automation tools manage routes, fuel usage, and maintenance. Higher AI capability levels support partial autonomy.
Self driving cars and fleet systems use sensors and machine perception to make decisions. Full autonomy remains limited by safety and regulation.
AI in Daily Life & Business
Daily tools use generative AI tools such as AI text generation and AI image generation. Platforms like Microsoft Copilot assist productivity and communication.
Businesses deploy AI powered assistants for customer service, analytics, and marketing. These systems improve efficiency but remain task-bound.
What Level of AI Is ChatGPT & What Comes Next?
ChatGPT operates within advanced Narrow AI. It uses large-scale language models to generate text but lacks true understanding. Within the Levels of AI, it aligns with Level 3 to Level 4 capabilities.
ChatGPT demonstrates impressive AI decision making and language synthesis. However, it does not possess human level intelligence or consciousness. Future systems may integrate reasoning, perception, and action, gradually moving toward AGI while remaining under human control.
Why Understanding AI Levels Matters
- 🎯 For Developers: Helps design systems with appropriate complexity and ethical safeguards.
- 🏢 For Businesses: Aligns investment with realistic AI capabilities.
- 📚 For Educators: Structures curriculum around current and emerging AI technologies.
- 🌍 For Society: Encourages informed debate on AI’s ethical and societal impact.
Levels of AI – Quick Answer
The levels of AI describe how intelligent or capable an artificial system is.
There are three primary levels:
| Level | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI) | Performs one task very well but can’t do others | Siri, Alexa |
| Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) | Understands, learns, and applies knowledge like a human | Still theoretical |
| Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI) | Exceeds human intelligence in all areas | Future vision (e.g., autonomous scientific AI) |
In short, AI evolves from basic task-specific tools to fully self-learning systems.
The Origin of “Levels of AI”
The term “levels of AI” originates from the conceptual models developed by early computer scientists in the 1950s and 60s. They wanted to classify AI according to its learning ability and autonomy. Over time, this framework evolved as researchers noticed that AI systems pass through stages—starting from simple automation to advanced reasoning.
While the phrase “levels of AI” is global, its use varies slightly between academic writing and tech journalism. Scholars use it for classification, while media outlets use it to simplify complex ideas for general readers.
FAQs About Levels of AI
What are the three levels of AI?
They are Narrow AI, General AI, and Super AI, representing increasing intelligence and autonomy.
What type of AI is ChatGPT?
ChatGPT is Narrow AI (ANI), also called weak AI, because it performs specific language tasks without true understanding or consciousness.
What are the 7 levels of AI?
The 7 levels of AI range from rule-based systems to theoretical Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) and Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI), showing how AI capability increases step by step.
What level of AI is ChatGPT?
ChatGPT fits between Level 3 and Level 4 AI, as it uses advanced machine learning and deep learning but lacks reasoning and self-awareness.
What are the 5 levels of AI?
The 5 levels of AI typically include reactive machines, limited memory AI, theory of mind AI, self-aware AI, and superintelligent AI.
What are the main types of AI?
The main types are Narrow AI (ANI), General AI (AGI), and Super AI (ASI), classified by how broadly an AI can think and act.
Conclusion
Understanding the Levels of AI helps make sense of how machines evolve from basic automation into advanced intelligence. These artificial intelligence levels reveal why today’s systems excel at specific tasks yet still fall short of true reasoning or consciousness. By viewing AI through capability stages, businesses, educators, and policymakers can adopt technology responsibly.
As the evolution of artificial intelligence continues, most tools remain within Narrow AI, including systems like ChatGPT. Future progress toward Artificial General Intelligence and Artificial Super Intelligence will reshape industries, ethics, and society. Knowing these levels today prepares us for smarter, safer decisions tomorrow.